Srinivas Konduri
Threws AI Community, Head
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing industries and shaping the future. However, as AI becomes increasingly integrated into our lives, the ethical implications it raises cannot be ignored. From biases in algorithms to concerns about job displacement, the ethical considerations surrounding AI are crucial for ensuring its responsible and beneficial development.
Unmasking Algorithmic Bias
One of the most pressing ethical challenges in AI is algorithmic bias. AI systems are designed to learn from data, and if that data contains biases, the AI can inadvertently perpetuate and even amplify them. Take, for instance, the case of biased hiring algorithms. If historical hiring data reflects bias against certain demographics, an AI system trained on that data might continue the discrimination, leading to a lack of diversity in the workplace. Ethical AI demands that developers actively address and mitigate biases, both in training data and algorithms themselves.
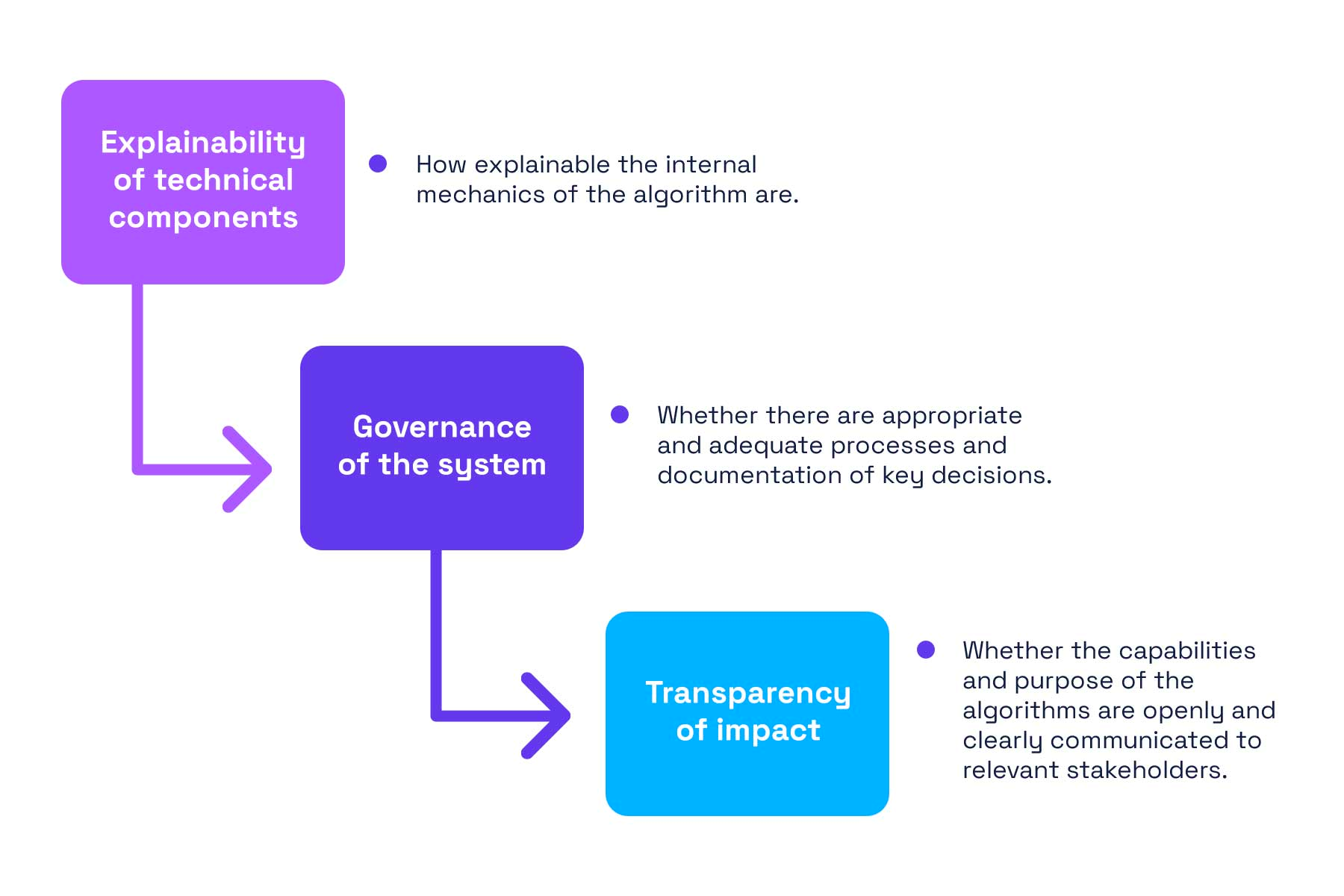
Transparency and Accountability
In an age where AI is making decisions that impact lives, transparency and accountability are paramount. The concept of the “black box” AI, where decisions are made without clear explanations, raises concerns about bias, fairness, and accountability. Ethical AI systems should be designed with transparency in mind, allowing users to understand how decisions are reached. Moreover, establishing clear lines of accountability is essential to prevent AI from becoming a scapegoat for unethical actions.
Job Displacement and Reskilling
AI’s potential to automate tasks that were once performed by humans has led to concerns about job displacement. While AI can lead to greater efficiency and innovation, it’s crucial to address the societal impact of job loss. Ethical considerations dictate that companies and policymakers should invest in reskilling and upskilling programs to ensure that the workforce remains relevant in the face of AI-driven changes.
Data Privacy and Security
Data is the lifeblood of AI, fueling the algorithms that power its decision-making processes. However, this reliance on data raises ethical questions about privacy and security.

Organizations must handle user data responsibly, ensuring that consent is obtained, data is anonymized when necessary, and security measures are robust to prevent breaches that could expose sensitive information.
Fairness and Justice
AI has the potential to reinforce or challenge existing social norms and systems. Ensuring fairness and justice in AI applications requires careful consideration of the broader societal implications. For instance, predictive policing algorithms might disproportionately target certain communities, leading to unjust outcomes. Ethical AI demands that fairness be a primary concern in algorithm design, with rigorous testing to identify and rectify any biased outcomes.
International Collaboration and Regulation
Given the global nature of AI development and deployment, international collaboration and regulation are vital. Ethical AI principles should transcend borders, ensuring that the responsible use of AI is upheld universally. Governments, tech companies, and researchers must work together to establish guidelines that prioritize human rights, safety, and fairness.
Conclusion
Ethics in AI is not an optional consideration; it’s an imperative. As AI continues to advance and reshape society, the decisions we make today will have far-reaching consequences. A future powered by ethical AI is one where technology enhances human potential, fosters inclusivity, and upholds the values that define our societies. By tackling algorithmic bias, prioritizing transparency, addressing job displacement, safeguarding data privacy, promoting fairness, and fostering international cooperation, we can navigate the ethical landscape of AI with wisdom and responsibility, shaping a better future for all.

